
Agonists and Antagonists – How we move
Muscles can only pull not push so therefore must work in pairs. While one contracts (agonist), the other lengthens (antagonist). Meanwhile others help the agonist (synergists). By knowing which muscles are do which roles we can look for imbalances and know when synergists have taken over and are causing issues.

How are long-term memories formed?
There are many theories on our long-term memories are formed. More recently researchers have proposed the concept of long-term potentiation. This is built on the premise that when we when we learn things we create a link between brain cells. The more we use this link, the stronger it becomes creating a long-term memory.
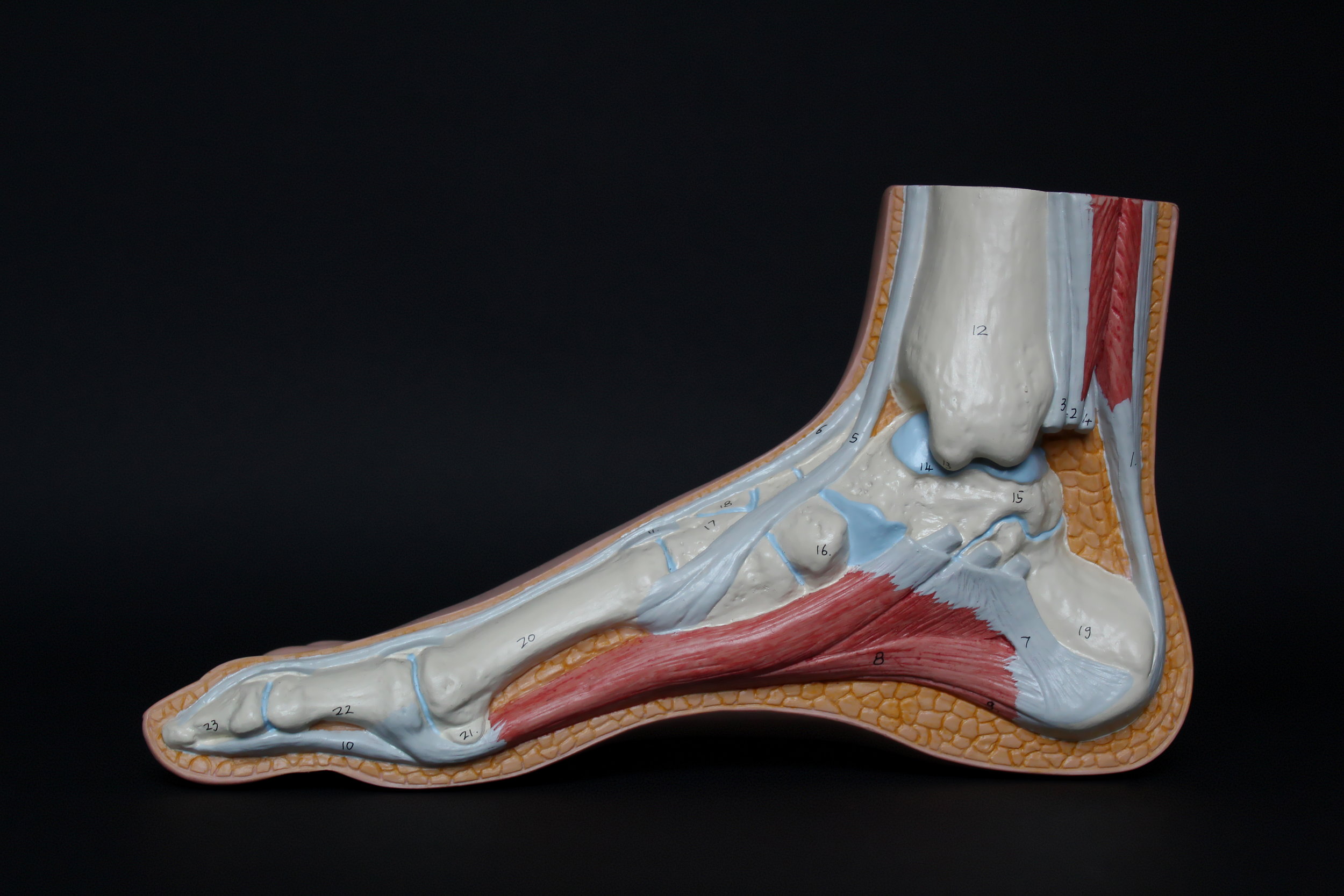
Tendon or Ligament? - What’s the Difference?
Ligaments and tendons have several key differences including where they are located and how they are injured. Despite this, they both look appear similar when they are injured and we can prevent injuring them and treat immediate injuries in very similar ways.

Implicit Memories - It’s about what you do not what you say
Implicit memory is also known as unconscious memory or automatic memory and are the memories that are hard to say.[i] It uses our past experiences to enable us to remember things without thinking about them. Procedural memories are a type of implicit memory. They include the skills we learn to such how to ride a bike or button a shirt. Learn more here

What’s your hardest working muscle?
When we think of exercise we often think of doing more and going harder. However, rest and recover are also vitally important. Without adequate recovery we cannot adapt and grow.
